Transformer:
A transformer is an electric power converter that transfers electrical power from one network to another through inductively di-coupled conductors-the transformer's coils. A varying current in the main or primary winding prepares a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a changing magnetic field through the secondary winding. That varying magnetic field produced a varying electromotive force (EMF), or "voltage", in the secondary winding. That effect is known as inductive coupling.
If a load is related to the secondary winding, current may goes in this winding, and electrical power will be transferred from the primary network through the transformer to the load. In an ideal transformer, the generated voltage in the secondary winding (Vs) is in proportion to the primary voltage (Vp) and is provided by the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary (Ns) to the number of moves in the primary (Np) as follows:
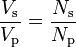
Browse important topics or keywords of Transformer below: