Rectification:
The hallmark of a rectifier diode is that it passes current in only one direction. This makes it useful for changing alternating current to direct current. Generally speaking, when cathode is negative with respect to anode, current flows; when cathode is positive relative to the anode, there is no current.
Assume that a 60-Hz ac sine wave is applied to input of circuit in Figure. During half cycle, the diode conducts, and during other half, it does not. Depending upon which way diode is hooked up, either positive half or the negative half of the alternating current cycle will be removed. Figure given below shows the output of the circuit at A. Keep in mind that that electrons flow from negative to positive, against arrow in diode symbol.
The circuit and wave diagram of the Figure given below shows a half-wave rectifier circuit. This
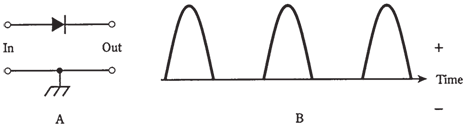
Figure-- At point A, half-wave rectifier. At point B, output of the circuit of A with sine-wave alternating current input.
is the simplest possible rectifier. That's its chief advantage over other, more complicated rectifier circuits.