The band model
The solids' band model is an extension of the molecular orbital (MO) technique. The overlap of atomic orbitals within an extended solid provides rise to continuous bands of electronic energy levels related with distinct degrees of bonding. The bottom of the band is made up of orbitals bonding among all neighboring atoms, in a simple monatomic solid; orbitals at the top of the band are antibonding and levels in the middle have an intermediate bonding character. Theoretically, distinct atomic orbitals can, give rise to dissimilar bands, even though they may overlap in energy.
The basic distinction among metallic and nonmetallic solids comes from the way where orbitals are filled. Metallic behavior results from a band partially occupied through electrons, therefore that there is no energy gap among the top filled level (known as the Fermi level) and the lowest empty one. Alternatively, a nonmetallic solid has a bandgap between an entirely filled band (the valence band VB) and an entirely empty one (the
conduction band CB). In a filled band the motion of any electron is matched by another one moving in the reverse direction, so that there is no net motion of electric charge. For conduction to take place in a nonmetallic solid, so, some electrons must be excited from the VB to the CB. This gives increment to an activation energy, and conductivity
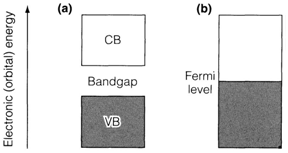
Fig. 1. Band picture for (a) nonmetallic and (b) metallic solid; occupied electronic levels are shown shaded.
increases with increment in temperature approximately in accordance with the Arrhenius equation employed in chemical kinetics.
Nonmetallic solids comprise covalent and ionic compounds. In the former case, the VB is made up of the top filled anion levels (example the 3p orbitals of Cl-, that are filled in making the ion) and the CB of the lowest empty cation levels (example in Na+ the 3s level from which an electron has been removed to make the cation). In covalent solids like diamond the VB contains bonding orbitals (example C-C) and the CB of antibonding orbitals.
Simple metallic solids are alloys or elements with close-packed structures in which the large number of interatomic overlaps gives rise to wide bands with no gaps among levels from distinct atomic orbitals. Though, Metallic properties can arise, in other contexts. In transition metal compounds a partially taken d shell can give rise to a partly filled band. So rhenium in ReO3 has the formal electron configuration 5d1 and is metallic. WO3 (formally 5d0) is not metallic but Na0.7WO3 is, like the electrons from sodium occupy the band made up of W 5d orbitals.