Perfect Bayesian Nash Equilibrium:
Our objective here is to find a perfect Bayesian Nash equilibrium. It would of course be useful to give a more precise statement of Requirement 4 - one that avoids the vague instruction "where possible". Here we consider a three- player game given in the figure below. This game has one sub-game that begins at player 2's singleton infonnation set. The unique Nash equilibrium in this sub-game between players 2 and 3 is (L, R'), so the unique sub-game perfect Nash equilibrium ofthe entire game is (D, L, R'). These strategies and the belief p = 1 for player 3 satisfy Requirement 1 through 3. They also trivially satisfy Requirement 4, since there is no information set off the equilibrium path, and so constitute a perfect Bayesian Nash equilibrium.
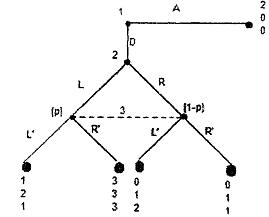
Now consider the strategies (A, L, L'), together with the belief p = 0. These strategies are a Nash equilibrium - no player wants to deviate unilaterally. These strategies and belief also satisfy Requirements 1 through 3 - player 3 has a belief and act optimally given it, and player 1 and 2 act optimally given the subsequent strategies of the other players. But this Nash equilibrium is not sub-game perfect, because the unique Nash equilibrium of the game's only sub-game is (L, R'). Thus, Requirements 1 through 3 do not guarantee that the player's strategies are a sub-game perfect ash equilibrium. The problem is that player 3's belief (p = 0) is inconsistent with player 2's strategy (L), but Requirements 1 through 3 impose no restrictions on 3's belief because 3's information set is not reached if the game is played according to the specified strategies. Requirement 4, however, forces player 3's belief to be determined by player 2's strategy: if 2's strategy is L then 3's belief must be p = 1; if 2's
strategy is R then 3's belief must be p = 0. But if 3's belief is p = 1, then Requirement 2 forces 3's strategy to be R'; so the strategies (A, L, L') with p = 0 do not satisfj Requirements 1 through 4 and therefore do not constitute a perfect Bayesian Nash equilibrium.