Balancing of Several Masses in Different Transverse Planes:
Now we will consider a case, where there are various masses in different planes.
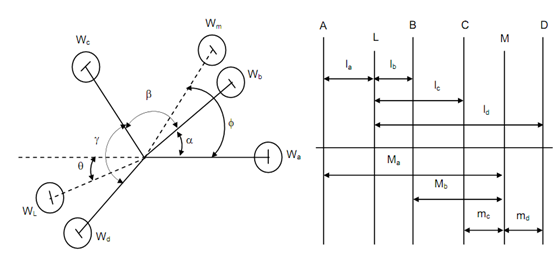
To start with, we shall name the planes in which masses revolve like A, B, C and D. The masses rotating in these planes are Wa, Wb, Wc and Wd respectively. The radii at which centres of gravity lie through axis of rotation in these planes are ra, rb, rc and rd respectively.
The angular separation among masses beginning from A and B are α, β and γ. The balancing masses shall be located in two planes L and M which are among A and B and among C and D, respectively. Figure 5 depicts the system. Distance among planes L and any of planes A, B, C and D is mentioned by l with suitable suffix. The similar distances for plane M is mentioned by m.
The method clearly is same as utilized in Section 19.3.1 in which balance masses in two planes L and M were found. So we have to repeat the process for mass in plane A and balancing mass in planes L and M. Therefore we proceed in steps of planes A, B, C and D. A table of the type shown below as Table 1 shall be helpful. Rows shall be devoted to planes in which masses revolve that could be known or unknown.
For a mass of weight W, revolving at radius r, the force is proportional to W r as ω2 /g is a constant. Two planes L & M are selected which are respectively at distances of l & m from the plane of revolving mass and balancing masses are located in planes L and M as given by Equation (6) and (7). Therefore the columns of the table shall describe plane (A, B, C, etc.) weight W; radius r; force W r; distances l and m; balancing forces in L and M.
Table 1: Calculation of Balancing Masses in Two Planes
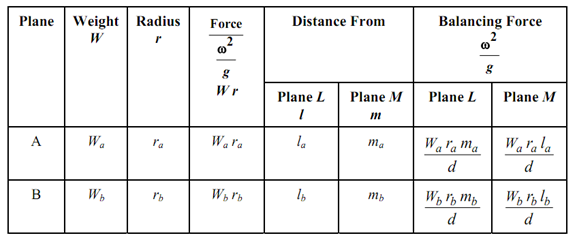
In last two columns the sign of the forces shall be decided by observation. Still as a rule if a force is in the similar direction as the disturbing force, then it shall be positive and if in the opposite direction it shall be -ve. After the balancing forces have been measured in planes L & M which shall be parallel to forces in planes A and B, etc. they are joints to provide a single resultant. Their inclination to force in plane A might be calculated.