Feed Drives - AC Servo Motors and Stepper Motors
AC Servo Motors
These are basically the AC synchronous motors with built-in brushless tacho and location encoders. The main advantage of this machine is the low rotor inertia and high power and low weight. It makes them very attractive since they are small in size compared to the equivalent DC servo motor.
Stepper Motors
A stepper motor rotates (steps) in fixed angular enhancement. Step size, or step angle, is determined by the construction of the motor and the type of drive scheme used to control it. Typical step resolution is 1.8 degrees (200 steps per rev). Through, micro-step motors are capable of 0.0144 degree steps (25 000 steps per rev). Micro-step motors are hybrid 200 step per rev motors that are electrically controlled to produce 25 000 steps per rev.
Stepper motors are usually used in open loop control systems as shown in Figure 3.1, though an encoder may be used to confirm positional accuracy. There are many types of step-motor construction. Though, permanent magnet (PM) and variable reluctance (VR) are the most common types.
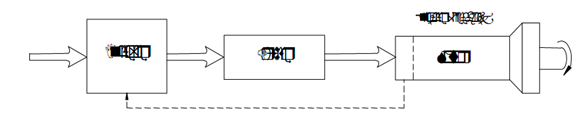
Figure 1: Typical Step Motor System. Precise Step Systems have Feedback Loop (Dotted Line) using Encoders or Resolvers