Design the strut:
Design the strut in Example if the two angles are placed on the same side of the 10 mm gusset plate.
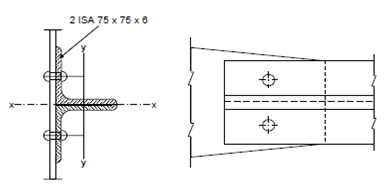
Figure
Solution
(a) Try two ISA angles 75 × 75 × 8 placed on the same side of the gusset plate as shown in Figure 6. The properties of the section are:
Area = 11.4 cm2, rxx= ryy = 2.28 cm, Cx= Cy = 2.14 cm.
The radius of gyration about axis xx
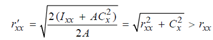
The radius of gyration about axis yy
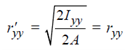
As rxx = ryy for the equal angles, the second case will give smaller value of radius of gyration (about y-y axis).
∴ rxx of the double angle section = 2.28 cm = 22.8 mm.
∴ As each angle is connected to the gusset plate by one rivet only the effective length is equal to actual length, i.e. leff = 2800 mm.
∴ Slenderness ratio, λ = 2800/22.8= 123 , for which corresponding
σac = 62 MPa.
Here the allowable stress will be 80% of σac.
∴ Pallowable = (0.8 × 62) × (2 × 1140) N =113 kN < 120kN ∴ rejected.
(b) Next try two ISA 80 × 80 × 8 sections similarly placed
Area = 2 × 12.2 cm2 = 2440 mm2, rxx = ryy = 2.44 cm
∴ λ = 2800/24.4 = 115, for which corresponding σac= 68 MPa.
∴ Pallowable = 0.8 × 68 × 2440 N = 132.7 kN.
As this is larger than the required 120 kN load, we have to accept it, as the standard section (IS angles) of next lower size (i.e. 2 nos ISA 75 × 75 × 8) was found to be insufficient.