Nucleosides:
In the RNA nucleosides have ribose as the sugar component and so are ribonucleosides. In DNA the sugar is deoxyribose for instance the 2'-OH group in ribose is replaced through a hydrogen atom; hence 'deoxy' and so the nucleosides are deoxynucleosides. For DNA that are deoxycytidine deoxyadenosine, deoxythymidine, and deoxyguanosine. In each case, the C-1 of the sugar is connects to the base via one of its nitrogen atoms if the base is a pyrimidine the
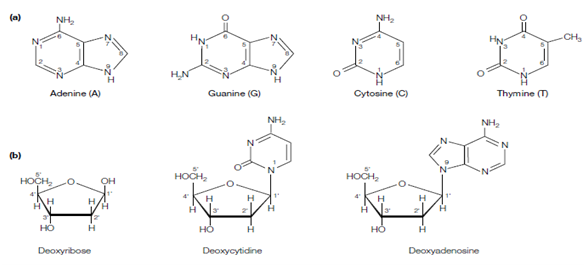
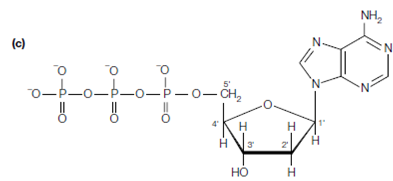
figure: (a) The purines, adenine and guanine, and the pyrimidines, thymine and cytosine; (b) deoxyribose and two deoxynucleosides, deoxycytidine and deoxyadenosine; (c) a deoxynucleotide, deoxyadenosine 5′-triphosphate (dATP).
nitrogen at the 1 position like N-1 is include in bonding to the sugar. If the base is a purine the bonding is to the N-9 position of the base shown in the figure.