Synthesis of nucleic acids by polymerases
All enzymatic extension of polynucleic acids requires a template and the synthesis of nucleic acids proceeds in a 5? to 3? direction. The RNA and DNA polymerases, in common with many other enzymes associated with nucleic acid metabolism, also require Mg2+ or a similar divalent ion to function. This ion is not strictly a prosthetic group for these enzymes, but helps in the binding of nucleotides to the active site. All the bacterial nucleic acid polymerases share a common structure in that the protein around the active site folds to form a structure that could be said to be like a hand. The template poly- nucleotide binds to the palm the active site and nucleotides enter among the thumb and forefinger.
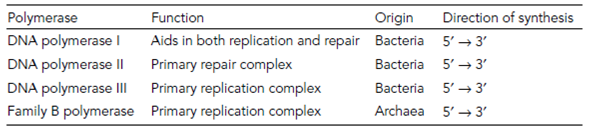
Bacterial cells have a variety of DNA polymerases in Table 1 each with specialized functions but most only have one RNA polymerase. In contrast most eukaryotes have a plethora of both specialized RNA and DNA polymerases. Unfortunately our knowledge of the cell biology of the Archaea is not sufficiently developed to be able to draw many inferences on this topic but we do know which their primary replicative polymerase resembles one class of eukaryotic DNA polymerase more than any of the bacterial types.
Table 1. Properties of bacterial and Archaeal DNA polymerases