DNA polymerases:
DNA polymerase I from E. coli catalyzes the stepwise addition of deoxyribonucleotides to the 3'-OH end of a DNA chain:
(DNA)n residues dNTP → (DNA)n + 1 PPi
The enzyme has the following needs that are as follows:
- All four dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dTTP and dCTP) must be present to be used as precursors; Mg2 is also needed;
- a DNA pattern is essential, to be copied through the DNA polymerase;
- a primer with a free 3'-OH in which the enzyme can extend.
DNA polymerase I is a sample-directed enzyme, which is it recognizes the next nucleotide on the DNA sample and then adds a complementary nucleotide to the 3'-OH of the primer, establishing a 3'5' phosphodiester bond and releasing pyrophosphate. The reaction is described in figure. It includes nucleophilic attack of the 3'-OH of the primer on the α-phosphate set of the incoming nucleotide. Primer is extended in a 5' → 3' that direction.
DNA polymerase I also corrects errors in DNA through erasing mismatched nucleotides example for it has proof-reading activity. Therefore, during polymerization, if the nucleotide in which has just been incorporated is incorrect mismatched, it is erased using the 3' → 5' exonuclease activity. that provides very high fidelity; a mistake rate of less than 10-8 per base pair. DNA polymerase also has a 5' → 3'exonuclease activity; it can hydrolyze nucleic acid beginning from the 5' end of a chain. This activity plays a key role in erasing the RNA primer used during replication. Therefore, whole, DNA polymerase I has three various active sites on its single polypeptide chain; 3' → 5' exonuclease 5' → 3' polymerase and 5' → 3' exonuclease. As well as its role in DNA replication, DNA polymerase I is included in DNA repair, for instance erasing UV-induced alterations like as pyrimidine dimers.
E. coli also contains two other DNA polymerase II, DNA polymerases III and DNA polymerase. As with DNA polymerase I that enzymes also catalyze the template-directed synthesis of DNA from deoxynucleotidyl 5'-triphosphates, require a primer with a free 3'-OH group, synthesize DNA in the 5' → 3' pathway and have 3' → 5' exonuclease activity. And enzyme has 5' → 3' exonuclease activity.
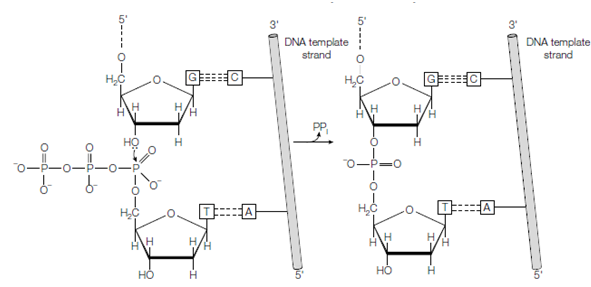
figure: DNA synthesis. In this schematic diagram, the incoming dTTP hydrogen bonds with the adenine on the template DNA strand and a 3 5 phosphodiester bond is formed, releasing pyrophosphate.