The relationship of purines to pyrimidines
The composition of DNA had been rigorously examined by Chargaff and colleagues in the late 1940s. They established that DNA had a set of properties, commonly known as Chargaff’s rules. These were as follows:
? The ratio of A to C to G to T varied between different species but not between individuals of the same species.
? The ratio of A to C and G to T did not vary among tissues of the similar individual and does not change with environmental conditions or age.
? In all DNA samples, the concentration of A was always the same as that of T, and the concentration of G was always the same as that of C generally summarized as A + G= T + C.
Structure of DNA could not have been worked out without these rules and the implications of the structure would not have been fully appreciated without the work on the transforming principle and interrupted T2 infection.
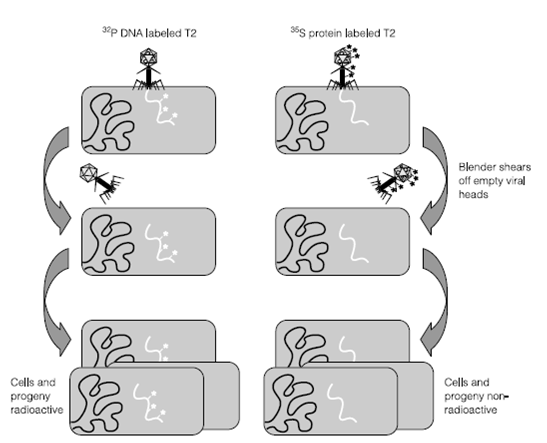
Figure . The Hershey–Chase experiment.