Curve of loading of an ion exchanger:
The D values are generally determined by batch method. A known amount of resin is brought in contact with a known amount of metal ion in solution until equilibrium is attained. Because isotherms are non-linear, a D values are taken to be limiting slopes at extremely low values. The best solution for this is to determine D values at low concentrations by taking labeled solutions using radioisotopes. The D value is determined by simply counting the solution before and after equilibrium with the resin.
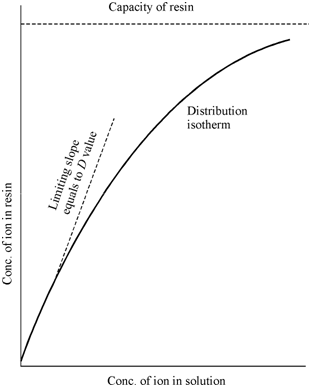
Figure: A typical curve of loading of an ion exchanger
Sometimes, the distribution ratio is expressed with different values, say
D = (Amount / L of wet volume)/(Amount / L of solution)
A conversion factor of D to Dv is a bed density, ρ, where ρ is in kg of dry resin per L of resin bed.
For any ion exchange, the importance is its use for the separation that means selectivity. For selectivity, the Dvalues should be different for the ions to be separated. It should be kept in mind that the Dvalues is conditional. It depends upon the nature of resin and the composition of the solution in contact with it. Composition will include pH, ionic strength, categories and molarity of acid and the presence of water miscible organic solvents and other ions.