Example of Dissociation Constant:
Example: The hydroxyl concentration [OH-] of a water solution o at 25ºC is 7.2 x 10-9 moles/liter. Calculate the pH of the solution.
Solution:
Kw =[H+] [OH-]
[H+] = Kw/[OH-] pH = -log [H+]
= 1× 10-14/7.2 × 10-9 = -log (1.38 × 10-6)
= 5.86
= 1.38 × 10-6
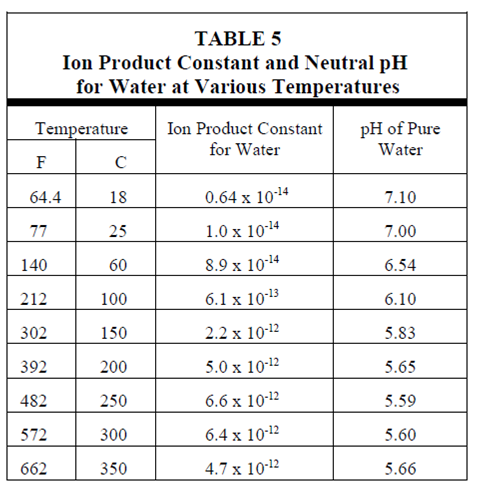
At 25ºC, equilibrium exists among pure molecular water and its ions. The [H+] equals the [OH-] and both have values of 1 x 10-7 moles/liter. By using the pH definition, it follows which the pH of pure water at 25ºC is 7. pH values less than 7 denotes an acidic solution and values greater than 7 denotes a basic or alkaline solution.
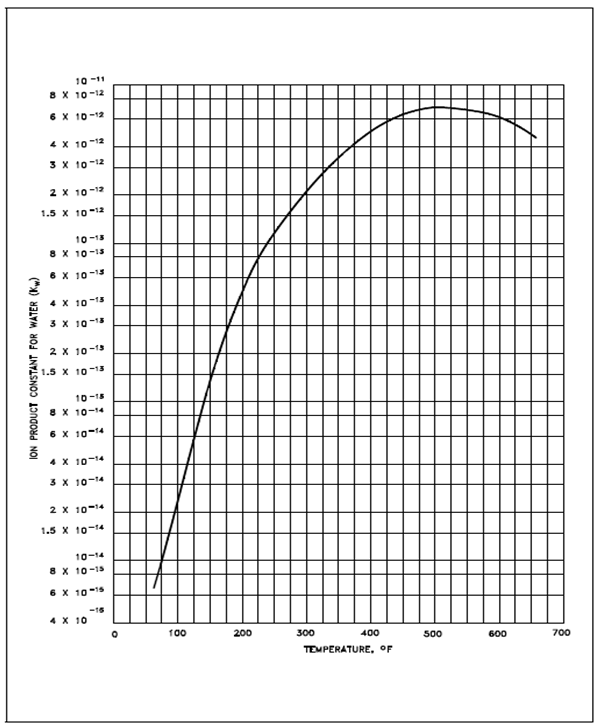
Figure: Ion Product Constant for Water