Limits
In earlier section we introduced you to the concept of a function & described various useful kinds of functions. In this topic, we regard the value "to which f (x) approaches as x get closer & closer to some number a". In inverted commas the phrase is to be understood intuitively & through practice. Here we do not give a formal definition. We call upon such a value the limit of f (x) and indicate it by limit .Sometimes this value cannot exist.
Example
Let the function f : R → R given by f (x) = x + 4. We desire to determine
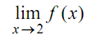
Solution
Look at Tables (a) &( b) . These give values of f (x) since x get closer and closer at 2 through values less than 2 & through values greater than 2, respectively.
Table a
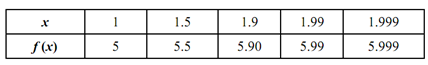
Table b
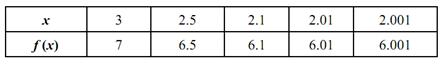
From the above two tables, it is apparent that as x approaches 2, f (x) approaches 6. Actually, the nearer x is selected to 2, the closer f (x) shall be to 6. Therefore, 6 is limit of x + 4 as x approaches 2, that is,
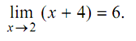
In the above example, the value of 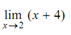 coincides with the value x + 4 when x = 2, that is,
coincides with the value x + 4 when x = 2, that is, 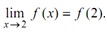
Numbers x close 2 fall into two natural categories; those which are less than 2, that is, those that lie to the left side of 2, and those which are greater than 2, that is, those which lie to the right side of 2.
We write
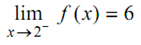
to denote that as x approaches 2 from the left, f (x) approaches 6.
We will describe this limit as the left-hand limit of f (x) since x approaches (or tends to) 2.
Likewise
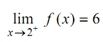
Mention that as x tends to 2 from the right, f (x) approaches 6.
We will call this limit like the right-handed limit of f (x) as x approaches 2. The left & right-hand limits are called upon one-sided limits.
It is apparent now that
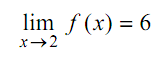
only if, both
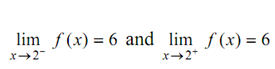
In the above instance, the value of 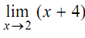 coincides along the value of X+4 when x = 2, which is
coincides along the value of X+4 when x = 2, which is

Similarly,
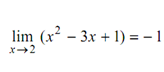
since also
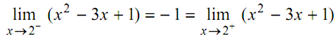
Now consider another function f : R - {2} → R given by 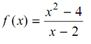
This function is not described at the point x = 2, as division by zero is not defined. But f(x) is described for values of x which approach 2. So it makes sense to appraise 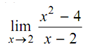
. Again, we let the given table (a) & (b) that give the values of f (x) as x approaches 2 through values < 2 & through values > 2, respectively.
Table a
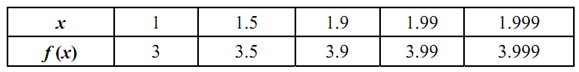
Table b
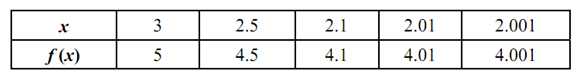
Since you may see
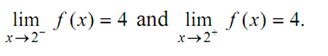
Thus, we shall say
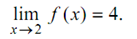
Now we are in a position to describe the limit of a function.
Consider f be a function & let a be a real number. We do not need that f be described at a, but we do need that f be described on a set of the form (a - p, a) ∪ (a, a +p).
(it guarantees that we may form f (x) for all x ≠ a which are "sufficiently close"
to a.)
Definition 6
f (x) is called to tend to the limit l as x approach a, written as
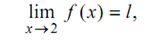
only if,
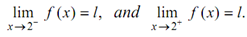
There is another definition to described limit of a function, equivalent to the above definition.
Definition 7
Assume f be a function described on some set (a - p, a) ∪ (a, a + p).
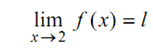
Only if, for each ε > 0 there present δ > 0 such that | f (x) - l | < ε
While 0 < | x - a | < δ. Note down that we do not deny that f can be possibly described at the point a. All we are stating is that the definition does not need it.