Fatigue Crack Propagation Mechanism
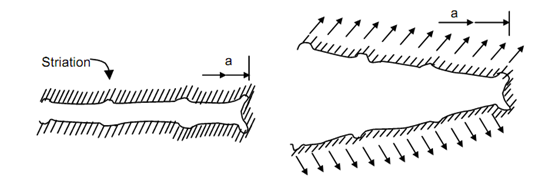
We talked of fatigue and its law of propagation earlier. In the section of fatigue it was pointed out that the fatigue fracture surface has characteristics appearance marked by conchoidal lines. These lines, also called striations, mark the arrest of crack and the distance between two consecutive striations is the crack extension during one load cycle. This has been confirmed by replica fractography and electron microscopy. The present text cannot deal with such methods and therefore these observations are simply referred to cursorily. Two similar models have been evolved for explaining the crack propagation for ductile and brittle materials. Very strong alloys come very close to definition of brittle material.
Figure shows a crack in which plastic deformation surrounds the crack tip. At (a) crack is under compression or zero loads. The two faces are parallel or in contact but the tip does not contact perfectly because some plastic strains do not recover. When crack faces are pulled apart under the effect of tensile stress, the shearing stresses acting at 45o to tensile stress help activate slip along 45o and the blunted crack tip extends in tip formation. The displacement at crack tip increases to accommodate the plastic deformation, as shown in Figure (b).
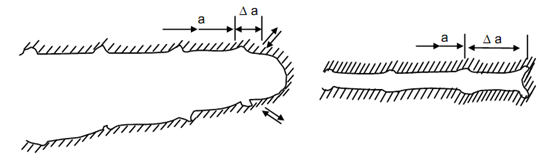
Further increase in tensile stress broadens the slip zone and reduces the stress concentration effect of the tip. This effectively results in blunting of crack tip into a semi circle ahead of previous crack tip. In subsequent stress reversal the faces of cracks are brought colder but the semi circle created in Figure (c) does not close sharply in a square end. The end carried two 45o lips because the slip zones does not recover as much as the central circular arc in Figure (d). Thus an additional step (or striation) is created along the crack length. Crack begins to open again in Figure (e) as the tensile stress begins to apply on crack faces.
One point may be noted with reference to Figure (d) that increases in crack length Δ a will depend very much upon the fact as to how much stress is applied upon two faces (compressive) to bring them closer. If the stress is small or zero or tensile then the crack tip will not blunt perfectly even if two crack faces come closer leaving semi-circular tip intact. It will require a few more cycles for creation of 45o lips at the crack tip. Apparently the higher fatigue strength in pulsating of fluctuating stress cycle is explained by this phenomenon.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)

(e)
Figure: Ductile Crack Extension Model
In high strength materials it will be cleavage fracture that will occur at 45o (approximately) because the slip zone will not be able to spread to the centre of the crack tip displacement. When a tensile stress begins to work one of the two cleavage cracks only will extend while the other will appear as striation. The model is illustrated in Figure.
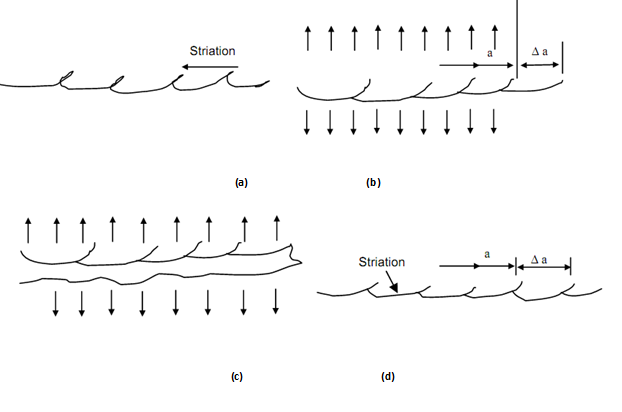
Figure: Brittle Crack Extension Model