Nmr spectrum of benzyl methyl ether:
The influence of diamagnetic circulation on aromatic protons is greater as compared to inductive effects and this can be seen in the nmr spectrum of benzyl methyl ether.
The methyl group at 3.6 ppm has a comparatively high chemical shift because of the inductive effect of oxygen. The methylene group at 5.2 ppm has an higher chemical shift because it is next to oxygen and the aromatic ring, both of which are electron withdrawing groups. Though, the aromatic protons have the highest chemical shift at 7.3 ppm as they experience the secondary magnetic field set up through diamagnetic circulation.
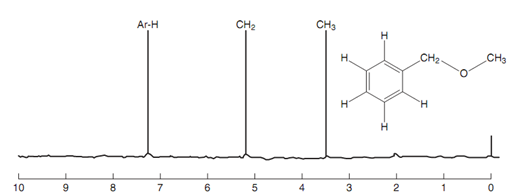
Figure: Nmr spectrum of benzyl methyl ether.
Diamagnetic circulation is as well possible for other unsaturated systems like alkenes. Though, the diamagnetic circulation for an alkene is much smaller because only two π electrons are circulating in a double bond, and thus the effect is smaller. This can be observed in the nmr spectrum of 1, 1-diphenylethene in which the alkene protons have a smaller chemical shift at 5.2 ppm as compared to the aromatic protons at 7.3 ppm.