Phototube:
A phototube consists of a photoemissive cathode and an anode in an evacuated tube along with a quartz window as display in Figure (a). These two electrodes are subjected to high voltage (about 100 V) difference. While a photon enters the tube and strikes the cathode, an electron is ejected and is attracted to the anode resulting in a flow of current that could be amplified and measured. The response of the photoemissive material is wavelength dependent and dissimilar phototubes are available for various regions of the spectrum.
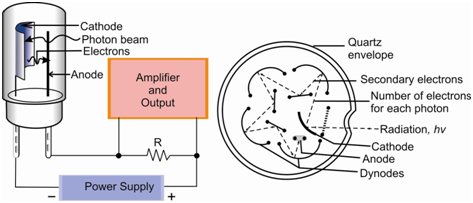
Figure: Detectors of UV-VIS radiation; a) Phototube and b) Photomultiplier tube