Gas flow rate:
If C is constant, then
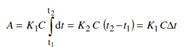
But C = M/V, therefore,
A = (K1 M/V) ?t
However, V= F, t, where F is carrier gas flow rate. Therefore, ?t e= V/F
And A = (K1 M/V)(V/F) = K1M/F
Thus, finally we obtain
A = K1M/F
Eq. 7.17 shows that peak area is directly proportional to the total mass of component. The above equation also shows that for a detector responding to concentration, the peak area is inversely proportional to the carrier gas flow rate. Thus, for accurate quantitative analysis along with TCD, a flow rate must be kept constant. For detectors responding to mass flow rate (dm/dt), such as the FID, we have
R= K2(dm/dt)
where, K2 is a constant of proportionality and m is the instantaneous mass of component within the detector, and R and t have their previous meaning. By similar purpose:
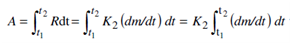
Cancelling dt within the integral sign, and integrating, we acquire
A=K2m
Eq. shows that for a detector responding to mass flow rate, the peak area is proportional to the total mass of the eluted solute. Therefore, unlike the concentration detector, the peak area for a mass flow detector is independent of carrier gas flow rate. Constant flow rate is not as critical for FID as for a TCD.
Figure: "Plug" flow