Gas Ionization Detectors:
These were the earliest detectors to be employed for the detection of radiations. When a radiation passes through a gas, some of its energy is deposited on the gaseous molecules which may ionize to form positive ions and electrons. If a suitable electric field is applied, the electrons or ions so formed generating a pulse can be related to the amount of radiations responsible for ionization.
A gas ionization detector consists of a cylindrical tube filled with a non conducting inert gas such as Ar or Xe and a central wire acting as anode. Metallic wall of the cylindrical tube acts as cathode. A classical detector system together along with its related electronics is display in Figure. While ionizing nuclear radiation passes through a thin window and interacts with the gas producing ion pairs, the ions are collected through the respective electrodes. A voltage pulse is generated that is measured.
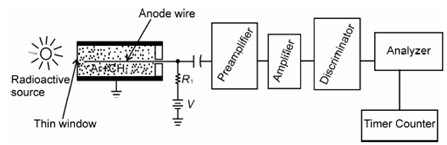
Figure: Block diagram of a typical gas ionization detection system showing various components