The Conceptual View
The Functional issues are treated using activities which represent the processing capabilities of the system. By Dealing with a customer’s confirmation request in an airline reservation system is an example of an activity as is updating the aircraft’s position in an avionics system. The Activities can be nested forming a hierarchy which constitutes a functional decomposition of the system. Items of information like as the distance to a goal or a customer’s name will typically flow among activities and might also be kept in data stores. Functional view of a system is captured with activity-charts that are same to conventional data flow diagrams.
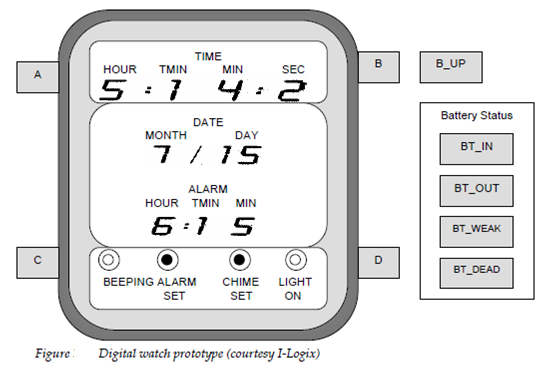
Dynamic behavioral issues are generally referred to as control aspects and are treated using state charts, the notation developed through Harel and his colleagues [HAR88] and [HAR92]. Here states can be linked and nested in a number of ways to represent concurrent or sequential behavior. An avionics mission computer for example could be in one of 3 states: air-to-ground, air-to-air or navigation. At the similar time it must be in the state of either manual or automatic flight control. Transitions among states are typically triggered through events that may be qualified through conditions. A Flipping is certain switch on the throttle for example it is an event which will cause a transition from the navigate stat to the air-to ground state but only on condition in which the aircraft has air-to-ground ammunition available. As an easy example consider the digital watch which is describe in figure . The State chart for the watch is described in figure .
Two views of a system are integrated in the subsequent way. Related with each level of an activity- chart there will generally be a state chart called a control activity whose role is to control the activities and data flows of that level this is same in some ways to the relationship among flow models and CSPEC define in chapter 12. The state chart is able to exercise control over the activities. Example For it can instruct activities to stop and start and to suspend and resume their work. It is able to modify the values of variables and therefore to influence the processing carried out through the activities. This is also able to send signals to other activities and therefore cause them to modify their own behavior. Additionally to being able to generate actions a controlling state chart is able to sense like this actions being carried out through other state charts. Example for, if one state chart starts an activity or increments the value of variable another can sense which event and use it say to trigger a transition.
It is important to realize in which activity-charts and state charts are linked strongly but they are not dissimilar representations of the similar thing. The Activity-charts on their own are incomplete as a model of the system still they do not address behavior. The State charts are also incomplete since without activities they have nothing to control. Mutually, a detailed activity-chart and its controlling state charts give the conceptual model. Activity-chart is the backbone of the model its decomposition of the capabilities of the system is the dominant hierarchy of the specification and its controlling state charts are the driving force beyond the system’s behavior.