Simulation and Modeling Techniques
The Mathematical analysis of a real-time system represents one approach which can be used to understand projected performance. Moreover, a growing number of real-time software developers use modeling and simulation tools which is not only analyze a system’s performance but also enable the software engineer to build a prototype and execute it and thereby gain an understanding of a system’s behavior.
The overall rationale beyond modeling and simulation for real-time systems is discussed [ILO89] through i- Logix (a organization which develops tools for systems engineers):
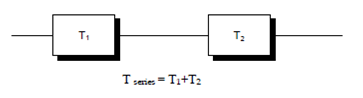
(a) Series rule - The arrivals are served by the subsystem in series.Tx = Time in system (delay)
(b) Parallel rule - The arrivals are served by the subsystem in parallel
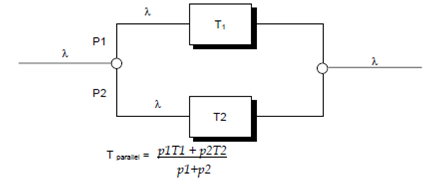
p1 = probability of entering the server 1 system.
P2 = probability of enterning the server 2 system
© Looping rule – A server with delay T T λ(μ) and a feedback loop with looping probability P
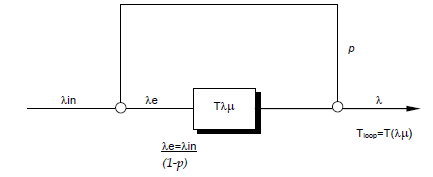
Figure Queuing network reduction rules
Understanding of a system’s performance in its environment over time is most often addressed in the implementation, design and testing phases of a project, by iterative error and trial. The Stalemate a system engineering tool for modeling and simulation approach gives an alternative to this costly procedure. It allows you to establish a comprehensive system model which is accurate enough to be relied on and clear enough to be useful. The model addresses the flow issues and usual functional but also covers the dynamic behavioral aspects of a system. This model can then be tested with the Stalemate retrieval and analysis tools that provide extensive mechanisms for debugging and inspecting the specification and retrieving data from it. Through testing the implementation model and the system engineer can see how the system as specified would behave if implemented.
i-Logix approach [HAR90] makes use of notation which combines 3 various views of a system that are: the module-chart the activity-chart and the state - chart. In the paragraphs which follows the i-Logix approach to real-time system modeling and simulation is described.