Conductometric methods:
Along With this background now we will see how dissociation of a weak electrolyte could be determined by using conductometric methods. The Ostwald derived a relationship among the molar conductivity and limiting molar conductivity. The molar conductivity of weak electrolyte can be expressed as the product of degree of dissociation of the electrolyte and it's limiting molar conductivity.
Λm = αΛ∝ or α = Λm/Λ ∝
This relationship is known as Ostwald relation. Substituting this in Eq. 6.3 gives.
Ka = ((Λm/ Λ ∝ )2 c)/1 - (Λm/ Λ∝ )
Rearrange Eq. (6.10) gives
Λm c= K a [(Λ ∝ )2/ Λm] -K a Λ∝
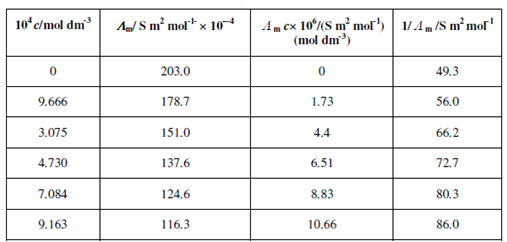
When we plot Λ mc against 1/ Λ m, we will get a linear plot with slope equal to Ka ( Λ ∝ )2. Therefore, Ka can be determined provided Λ∝ is known. Therefore, we could use this method for the determination Ka. of weak acids and bases. To further understand this, let us consider the dissociation of nitric acid in methanol over a wide range of concentration (see Table 6.1). In methanol nitric acid acts as a weak electrolyte and therefore, we can use Eq. (6.12) to determine the dissociation constant Ka.
Table: Molar Conduvtivity values of Nitric Acid in Methanol