Generator Action in a Motor
A generator action is established in each motor. Whenever a conductor cuts lines of force, an EMF is induced within conductor.Current to begin the armature turning will flow in the direction determined through the applied DC power source. After rotation begins, the conductor cuts lines of force. Through applying the left-hand rule for generators, the EMF which is induced in the armature will generates a current in the opposite direction. An induced EMF, as a result of motor operation, is known as counterelectromotive force, or CEMF, as describes in Figure.
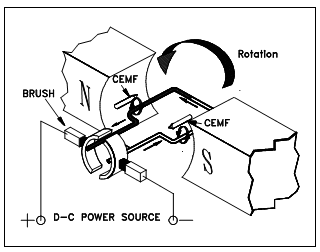
Figure: Counterelectromotive Force (CEMF)
Because the CEMF is produced through the action of the armature cutting lines of force, the value of CEMF will depend on field strength and armature speed, as display in Equation (6-2).
ECEMF = K Φ N (6-2)
where
ECEMF = counter EMF
K = constant
Φ = field flux strength
N = speed of the armature
The CEMF opposes the applied functions and voltage to lower armature current. Effective voltage acting in the armature of a motor is the applied voltage, minus the counter EMF. The Armature current could be found through using Ohm’s law, as display in Equation (6-3).
Ia = Et – ECEMF/Ra (6-3)
where
Ia = armature current
Et = terminal voltage
ECEMF = counter EMF
Ra = armature resistance