Temperature Coefficient of Resistance:
Temperature coefficient of resistance, α (alpha), is declared as the amount of modify of the resistance of a material for a given modification in temperature. A positive value of denotes in which R increases along with temperature; a negative value of denotes R decreases; and zero denotes which R is constant. Classical values are listed in Table 2.
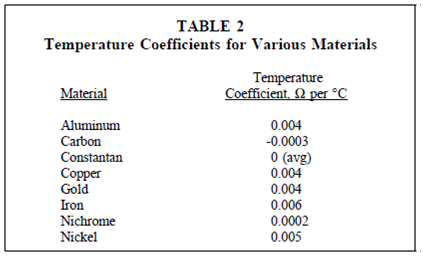
For a given material, may vary with temperature; therefore, charts are often used to describe how resistance of a material varies with temperature.
An increase in resistance can be approximated from equation (2-2).
Rt = Ro +Ro(αΔT) (2-2)
where
Rt = higher resistance at higher temperatures
Ro = resistance at 20oC
α = temperature coefficient
T = temperature rise above 20oC