Voltage across every resistor:
A 120 V battery is linked in series along with three resistors: 40Ω, 60Ω, and 100Ω in the Figure. Find out the voltage across every resistor.
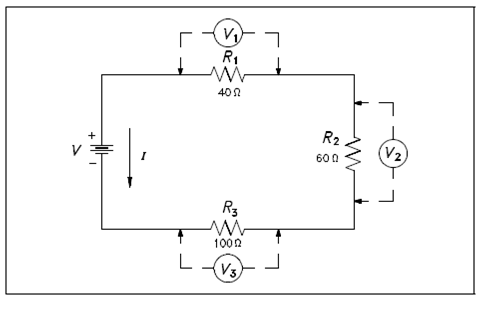
Figure: Example 2 Series Circuit
Solution:
Step 1: Find total resistance.
RT = R1 + R2 + R3
RT = 40 Ω+ 60 Ω+ 100 Ω
RT = 200 ohms
Step 2: Find circuit current (I).
VT = IRT
Solving for I:
I=VT/RT
I= 120 volts/200Ω
I= 0.6 amps
Step 3: Find out the voltage across every component.
V1 = IR1
V1 = (0.6 amps)(40 Ω)
V1 = 24 volts
V2 = IR2
V2 = (0.6 amps)(60 Ω )
V2 = 36 volts
V3 = IR3
V3 = (0.6 amps)(100 Ω )
V3 = 60 volts
The voltages of V1, V2, and V3 in Example 2 are called as "voltage drops" or "IR drops." Their effect is to decrease the available voltage to be applied across the other circuit components. A sum of the voltage drops in many series circuits is always equal to the applied voltage. We could verify our answer in Example 2 through using equation (2-4).
VT =V1 +V2 + V3
120 volts = 24 volts+ 36 volts+60 volts
120 volts = 120 volts