Resistance in Parallel:
Total resistance in a parallel circuit could be found through applying Ohm's Law. Divide of the voltage across the parallel resistance through the total line current as display in the given equation (2-9).
RT = V/ IT (2-9)
Example: Find out the total resistance of the circuit display in Figure if the line voltage is 120 V and total current is 26A.
RT = V/ IT = 120/26 =4.62 ?
The total load connected to a 120 V source is the similar as the one "equivalent resistance" of 4.62 ? which was connected across the source display in the given figure. Equivalent resistance is the total resistance a combination of loads present to a circuit.
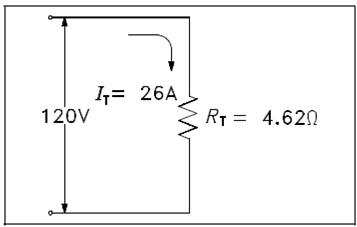
Figure: Equivalent Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
The total resistance in a parallel circuit could also be found through using the equation (2-10).
1/RT =1/R1 +1/R2+1/R3 + ... 1/RN (2-10)
Example: Find the total resistance of a 4 ?, an 8 ?, and a 16? resistor in parallel (Figure 27).
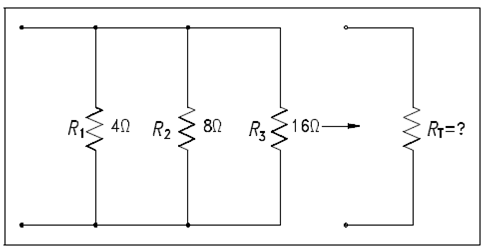
Figure: Total Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
Solution:
1/RT =1/R1 +1/R2+1/R3
1/RT =1/4 +1/8+1/16
1/RT =4/16 +2/16+1/16 = 7/16
RT =16/7 = 2.29?
Note: Every time you like resistors are in parallel, the total resistance is always smaller than any single branch.