Current Division:
Sometimes it is necessary to search out the individual branch currents in a parallel circuit when just resistance and total current are known. When only two branches are included, the current in one branch will be a few fraction of IT. A resistance in every circuit could be used to divide the total current into fractional currents in every branch. This procedure is known as current division.
I1 = R2/ R1+R2 IT
I2 = R1/ R1+R2 IT (2-13)
Note that the equation for every branch current has the opposite R in the numerator. This is since each branch current is inversely proportional to the branch resistance.
Example: Find out branch current for I1 and I2 for the circuit display in Figure.
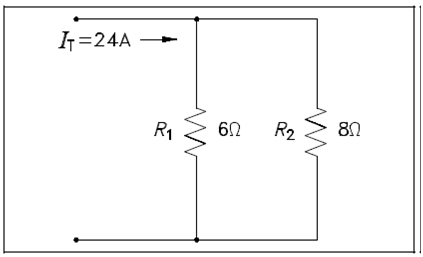
Figure: Current Division Example Circuit
Solution:
I1 = R2/ R1+R2 IT =8/6+8 (24) =8/14(24) =13.71 amps
I2 = R1/ R1+R2 IT =6/6+8 (24) =6/14(24) =10.29 amps
Since I1 and IT were known, we could have also simply subtracted I1 from IT to find out I2:
IT = I1 + I2
I2 = IT - I1
=24- 13.71
=10.29 amps