Series-Parallel Circuit Analysis:
When solving for current, voltage, and resistance in a series-parallel circuit, follow the rules that apply to the series part of the circuit and follow the rules which apply to the parallel part of the circuit. By Solving these circuits could be simplified through decreasing the circuit to a single equivalent resistance circuit, and redrawing the circuit within simplified form. The circuit is then known as an equivalent circuit that was describe in the above Figure.
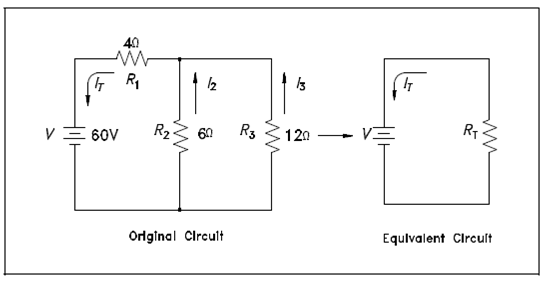
Figure: Redrawn Circuit Example
The easiest way to solve these categories of circuits is to do it in steps.
Step 1: Find out the equivalent resistance of the parallel branch:
RP = R2 R3 /R2 + R3 = (6) (12) /6 + 12 = 72 /18 = 4?
Step 2: Find out the resistance of the equivalent series circuit:
RT = R1 + RP = 4? + 4? = 8 ?
Step 3: Find total current (IT):
IT = V/RT = 60 V /8? = 7.5 amps
Step 4: Find out I2 and I3. The voltage across R1 and R2 is equal to the applied voltage (V), minus the voltage drop across R1.
V2 = V3 = V - ITR1 = 60 - (7.5 X 4) = 30 V
Then, I2 and I3 are calculated.
I2 = V2/R2 = 30 /6 = 5 amps
I3 = V3/R3 = 30 /12 = 2.5 amps