Transmission media
Data is transmitted over various different media. The common are cable, radio, satellite links, and fiberoptics. Cable and satellite communications use radio-frequency spectrum. Fiberoptics makes use of infrared or visible light energy.
Cable
The earliest cables were wires which carried direct current. Nowadays, data transmission cables often carry alternating current at radio frequencies. One advantage of using RF is that signals can be amplified at intervals on a long span. This largely increases the distances over which data is sent by cable. Another advantage of using RF is that several signals can be carried over the single cable, with each signal on a different frequency.
Cables consist of pairs of wires, akin to lamp cords. But often coaxial cable is used. This has center conductor surrounded by the cylindrical shield. The shield is grounded, and center conductor carries signals. The center conductor is kept in place by the insulating dielectric, usually made of polyethylene. The shield keeps signals confined to cable, and keeps external electromagnetic fields from interfering with signals.
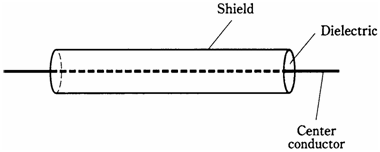
Figure-- A coaxial cable has a center conductor surrounded by cylindrical shield.
Cable signals are modulated by using any of techniques which were outlined earlier.
Radio
All the radio and TV signals are electromagnetic waves. The radio/TV transmitter output is coupled into antenna system located at a distance from the transmitter. The energy follows transmission line, called as feed line, from the transmitter PA output to antenna itself.Most of the transmission lines are coaxial cables. There are other types, used in the special applications. At the microwaves, hollow tubes called as waveguides are used to transfer energy from a transmitter to antenna. A waveguide is quite efficient than coaxial cable at shortest radio wavelengths.
Radio amateurs use parallel-wire transmission lines, resembling ribbon cable popular for use with the consumer TV receiving antennas. In the parallel-wire line, the RF currents in 2 conductors are always 180 °out of phase, such that their electromagnetic fields cancel each other. This keeps transmission line from radiating, guiding EM field toward the antenna. The energy can be radiated when it reaches the antenna.The radio frequency bands are categorized generally from very low frequency (VLF) through microwaves, according to breakdown in the. These waves propagate through atmosphere, or through space, in different ways depending on frequency.
|
Classification
Very Low Frequency
|
Abbreviation
VLF
|
Frequency range
9 kHz and below
|
|
Low Frequency (Longwave)
|
LF
|
30 kHz–300 kHz
|
|
Medium Frequency
|
MF
|
300 kHz–3 MHz
|
|
High Frequency (Shortwave)
|
HF
|
3 MHz–30 MHz
|
|
Very High Frequency
|
VHF
|
30 MHz–300 MHz
|
|
Ultra High Frequency
|
UHF
|
300 MHz–3 GHz
|
|
Microwaves
|
|
3 GHz and above
|
Satellite links
At very high frequencies (VHF) and above, communications circuits use satellites in geostationary orbits around earth. If the satellite is directly over equator at an altitude of 22,300 miles and this orbits from west to east, it will follow the earth rotation, staying in same spot in sky as seen from surface.A single geostationary satellite is on the line of sight with around 40 % of the earth’s surface. Three such type of satellites, placed at 120-% (1/3-circle) intervals around planet, allow coverage of all the populated regions. A dish antenna can be aimed at the geostationary satellite, and once antenna is in place, it is not required be turned or adjusted. Perhaps you have satellite TV system.
Fiberoptics
A beam of infrared or visible light is modulated just as can radio frequency carriers. The frequencies of infrared and visible light are very high, allowing the modulation by data at rates into gigahertz range.A simple modulated-light transmitter can be diagrammed schematically in the figure given below. The output of light emitting diode (LED) is modulated by audio from transistor. The light is guided into the optical fiber, made from the special mixture of very clear glass. In the recent years, fiberoptics has begun to replace conventional cable networks on the massive scale.Fiberoptics has several advantages over wire cables. A fiberoptic cable is cheap, and it is light in weight. It is totally immune to the interference from outside electromagnetic fields. A fiberoptic cable will not corrode as the metallic wires do. Fiberoptic cables are not expensive to maintain and simple to repair. An optical fiber can carry far more signals than a cable, as the carrier frequency is practically infinite. The whole radio spectrum, from VLF through microwaves, are imprinted on a beam of light and sent through single glass fiber no thicker than strand of your hair.
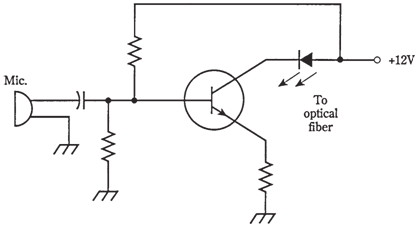
Figure--A simple circuit for voice modulating the light beam