Single sideband
As mentioned earlier, AM is not efficient. Most of the power is which is used up by the carrier; only 33 % of it carries data. Besides that, the 2 sidebands are the mirror-image duplicates. An AM signal is redundant, as well as inefficient, for the voice transmission.
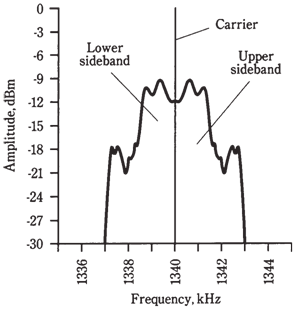
Figure--Spectral display of a typical voice AM signal
Voice SSB
During fifties, engineers began to work on the alternative to conventional AM. They mused, Assume that all the transmitter power could go into voice, and none be taken up by carrier? That would be the threefold effective increase in transmitter power! And what if bandwidth could be cut to 3 kHz instead of 6 kHz, by getting rid of the sideband redundancy? That would put all energy into half spectrum space, so that twice voice signals could fit in the band. Spectrum-space conservation was becoming a big deal. The airwaves were beginning to become overcrowded.The improvements were realized by circuits which cancel out, or suppress, the carrier in modulator circuit, and that filter out, or phase out, one of the 2 sidebands. The remaining voice signal has a spectrum display which looks like the graph of the figure given to us. Either LSB or USB is used, and either of the mode works as well as the other.
The SSB transmitter
The center of an SSB transmitter is a balanced modulator. This circuit works like a normal AM modulator, except that carrier wave is phased out. This leaves LSB and USB. One of the sidebands can be removed by a filter which passes only the RF within the 3-kHz-wide band. The block diagram of the SSB transmitter is shown in the figure given below.
High-level modulation will not work for SSB. The balanced modulator is in the low power part of transmitter. Thus, the RF amplifiers after modulator should be all linear. They usually work in class A except for PA, which is class AB or class B. If the class-C amplification is used with the SSB signal, or if any of RF amplifiers are not linear for any reason, signal envelope will be distorted. This will degrade quality of signal. It can also make bandwidth to exceed the nominal3 kHz,resulting in the interference to other stations by using the band.
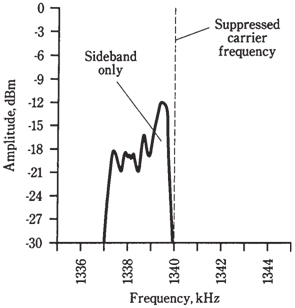
Figure--Spectral display of a typical voice SSB signal.In this case, it is lower sideband.
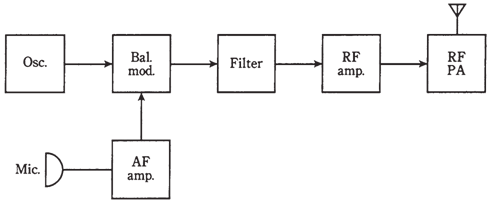
Figure-- An SSB transmitter