Frequency and phase modulation
AM and SSB both work by varying signal strength. This can be a basic disadvantage when there is sferic noise created by thundershowers in vicinity. Sferics are recognizable as crashes or crackles in SSB receiver. Ignition noise can be a problem;this sounds like a buzz. Sferics and ignition noise are both predominantly amplitude modulated.
In frequency modulation (FM), amplitude of signal remains constant, and instantaneous frequency or phase is made to change. As the carrier is always full on, class-C power amplifiers are used. Linearity is of no concern when signal level does not change.
Reactance modulation versus phase modulation
The most direct way to obtain FM is to apply audio signal to a varactor diode in a VFO circuit. An instance of this scheme, called as reactance modulation, is shown in the figure given below. The varying voltage across varactor causes its capacitance to change in accordance to the audio waveform. The change in capacitance results in an up and down swing in frequency which is generated by VFO. In the illustration, only tuned circuit of the Hartley oscillator is shown.
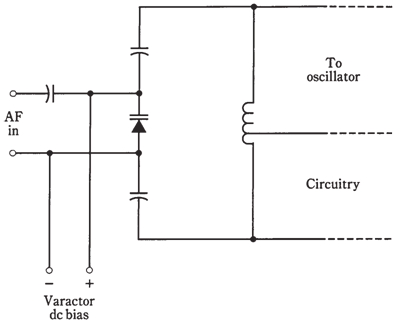
Figure--Reactance modulation to obtain FM.
Another method to get FM is to modulate the phase of oscillator signal. This causes small fluctuations in frequency as well, as any instantaneous phase change shows up as an instantaneous frequency change. This scheme is called as phase modulation. The circuit is much more complicated than reactance modulator. When the phase modulation is used, audio signal should be processed, adjusting amplitude versus frequency response of audio amplifiers. Else the signal will sound muffled in an FM receiver.
Frequency deviation
The amount by which carrier frequency varies will depend on relative audio signal level, and also on degree to which audio is amplified before it is applied to modulator. The deviation is maximum extent to which the instantaneous carrier frequency differs from unmodulated carrier frequency. For most of the FM voice transmitters, deviation is standardized at plus or minus 5.0 kHz.
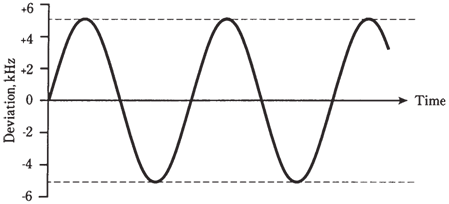
Figure--Frequency-versus-time rendition of an FM signal.
The deviation obtainable by the direct FM is greater, for the given oscillator frequency, than deviation which can be gotten by means of phase modulation. But deviation of the signal can be increased by frequency multiplier. This is an RF amplifier circuit the output of which is tuned to some integral multiple of input. A multiply by two circuit is known as frequency doubler; a multiply by 3 circuit is a frequency tripler.When the FM signal is passed through the frequency multiplier, deviation gets multiplied with the carrier frequency. If the modulator gives plus or minus 1.6 kHz deviation, the frequency is doubled and the result will be a deviation of plus or minus 3.2 kHz. If frequency is tripled, deviation increases to plus or minus 4.8 kHz, which is about the standard amount for FM voice communications.
Wideband FM
In the FM hi-fi broadcasting, and in some other applications, deviation is much greater than plus or minus 5.0 kHz. This is called as wideband FM, as opposed to narrowband FM as discussed.For the ordinary voice communications, there is nothing to be gained using wide band FM. The result will be that the signal will take up an needless amount of radio spectrum space. But for the music, the fidelity improves as bandwidth increases.The deviation for the FM signal should be equal to highest modulating audio frequency, if the optimum fidelity is to be obtained. Thus the, plus or minus 5.0 kHz is enough for voice (3.0 kHz would probably suffice). For the music, a deviation of around plus or minus 15 kHz or 20 kHz is required for excellent hi-fi reception.
The ratio of frequency deviation to highest modulating audio frequency is called as modulation index. For good fidelity, it must be at least 1: 1. But it should not be more; it would waste spectrum space.