Possible cases:
The nature of this solution based on the term in the square root. There are three following possible cases:
(1) (c/m) 2 > 4 (k /m) - Overdamped case
(2) (c/m)2 = 4 (k/m) - Critically damped case
(3) (c/m)2 < 4 (k/m) - Underdamped case
Let the critical damping coefficient be Cc, Hence,
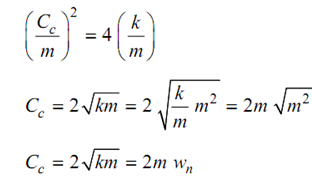
Almost all of the systems are underdamped.
Here,
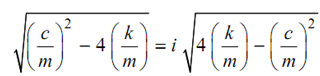
The ratio of damping coefficient (c) to critical damping coefficient is known as damping factor 'J'.
J = C /Cc . . . (17)
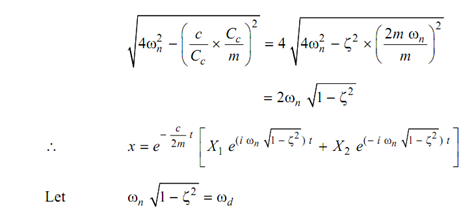 .....(18)
.....(18)
here ωd is natural frequency of the damped free vibrations.
Hence, underdamped case
x = e - (c /2m) ( X1 ei ωd t + X e- i ωd t ) . . . (19)
For critically damped system
x = ( X1 + X 2 t ) e - ( c/2m) t
For overdamped system
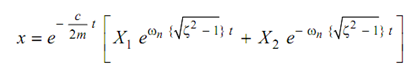 . . . (20)
. . . (20)
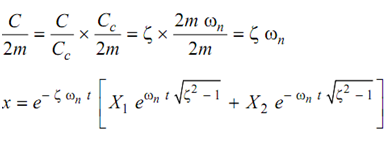 . . . (21)
. . . (21)
Figure
The Equation (19) may also be written as
x = X e-ζ ωn t cos (ωd t + φ) . . . (23)
Here X and φ are constants. X represents amplitude and φ phase angle.
Assume at t = t, x = x0.
∴ x0 = X e- ζ ωn t cos (ωd t + φ) . . . (24)
After one time period
t = t + t p and x = x1
∴ x = X e- ζ ωn (t + t p ) cos {ωd (t + tp ) + φ} . . (25)
Dividing Eq. (24) by Eq. (25)
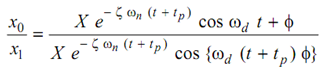
As
t p = 1/ f p = 2π/ ωd
or ωd t p = 2π
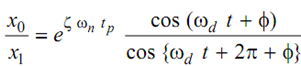
Since cos θ= cos (2π+ θ)
∴ cos (ωd t + φ) = cos {ωd t + 2π + φ}
∴ x0 /x1 = e ζ ωn t p
or L = x0 /x1= ζ ωn tp = ζ ωn (2π/ ωd )=
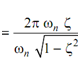
or
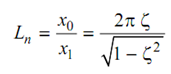 -------- (26)
-------- (26)
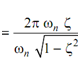 is known as logarithmic decrement.
is known as logarithmic decrement.
If at t = t + n t p
It might be proved that
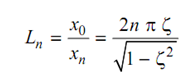 --------(27)
--------(27)
If
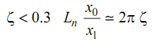
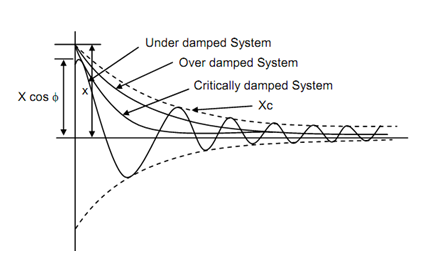
Figure 8 shows displacement time diagram for the above indicated three cases. For critically damped & overdamped system mass returns to its original place (indisplaced) gradually and there is no vibration. Vibration is possible just in the underdamped system as the roots of Eq. (14) are hard and solution consists of periodic functions (Eq. (22)).