Muscle structure
In biological systems, the best understood force-generating procedure is the contraction of vertebrate striated muscle, so named because it appears striated (striped) under phase-contrast microscopy. This muscle is composed of numerous multinucleate cells that are limited by an electrically excitable plasma membrane. Each cell consists within its sarcoplasm (cytosol) various parallel myofibrils, each about 1 μm in diameter. The sarcoplasm is rich in ATP also, creatine phosphate and glycolytic enzymes. Sarcomere is functional unit of the myofibril which repeats every 2.3 μm along the fibril axis. A dark A band and a light I band regularly alternate along the length of the myofibril. The central region of the A band is the H zone which is less dense than the rest of the band. In the middle of I band is a very thick narrow Z line. A cross-section of a
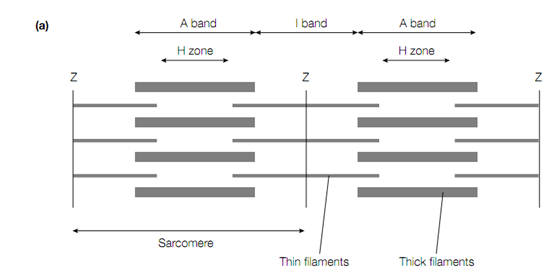
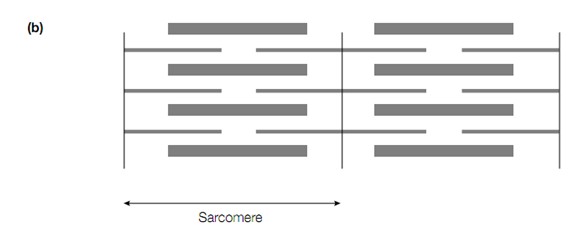
Schematic diagram showing the appearance of vertebrate striated muscle as it appears under phase-contrast microscopy. (a) Relaxed, (b) contracted.
myofibril reveals that there are 2 types of interacting filaments. The thick filaments of diameter about 15 nm are found in the A band only and consist primarily of the protein myosin, whereas the thin filaments of approximately 9 nm diameter which contain, tropomyosin, actin & the troponin complex.
When muscle contracts it may shorten by as much as a third of its original length. Information got from X-ray and light and electron-microscopic studies led to the proposal of the sliding ?lament model to describe muscle contraction. During muscle contraction The thin and thick filaments were seen not to change in length, but the length of the sarcomere was observed to decrease as the thin and thick filaments slide past each other therefore, as muscle contracts, the sizes of the I band and the H zone are seen to decrease. The force of the contraction is produced by a procedure that actively moves one type of fiament past neighbouring filaments of the other type.