The generation of force in muscle
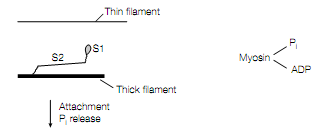
The cyclic formation and dissociation of cross-bridges between the S1 and actin heads of myosin leads to contraction of the muscle because of conformational changes that occur in the myosin S1 head. The S1 heads are unable to interact with the actin in the thin filaments by the regulatory protein tropomyosin because of steric inter- ference in resting muscle. The myosin has bound to it Pi and ADP. The tropomyosin moves out of the way, when the muscle is stimulated, permitting the S1 heads projecting out from the thick filament to connect to the actin in the thin filament. First the Pi and then the ADP are released on binding of myosin-ADP-Pi to actin. The S1 head undergoes a conformational change as the ADP is released, in the hinge region between the S2 and S1 domains that alters its orientation relative to the actin molecule in the thin fiament. This constitutes the power stroke of muscle contraction and
(a)
(b)
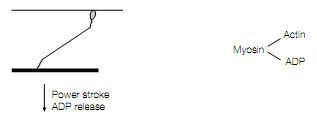
(c)

(d)
(e)

For the generation of force, Mechanism in muscle as an S1 head of a myosin thick filament interacts with an actin thin ?lament.
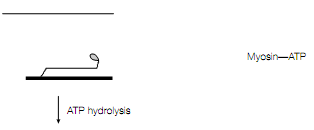
results in the thin filament moving a distance of about 10 nm relative to the thick fiament towards the centre of the sarcomere. Then ATP binds to the S1 head which leads to the rapid release of the actin [for example dissociation of the thin and thick filaments ]. Then The ATP is hydrolyzed to Pi and ADP by the free S1 head, which is returned to its original conformation ready for another round of attachment, conformational change and release.