Actin
Actin is the major constituent of the thin filaments which exists in 2 forms. In solutions of low ionic strength it present as a 42 kDa monomer which termed as G-actin because of its globular shape. Since the ionic strength of the solution rises to that at the physiological level, G-actin polymerizes into a fibrous form called F-actin that resembles the thin filaments found in muscle. Although actin, such as myosin, is an ATPase, the hydrolysis of ATP is not involved in the contraction relaxation cycle of muscle but rather in the disassembly and assembly of the actin filament. Cross-bridges emerge from the filament axis on the thick filaments, in a regular helical array towards either end, whereas there is a bare region in the middle that is devoid of cross-bridges. In muscle depleted of ATP, the myosin cross-bridges interact with the surrounding actin filaments. The absolute
(a)
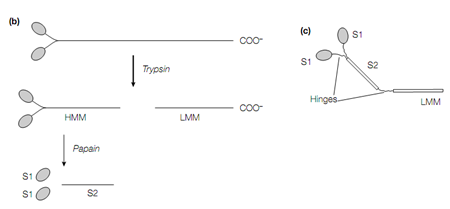
Structure of myosin (a) showing the association of the two heavy and two pairs of light chains, (b) showing the proteolytic fragmentation of myosin, and (c) showing the hinge regions between domains.
direction of the myosin and actin molecules reverses halfway between the Z lines. therefore, as the 2 thin filaments that bind the cross-bridges at either end of a thick filament move towards each other, sliding over the thick filament, the distance between the muscle contracts and the Z lines shortens.
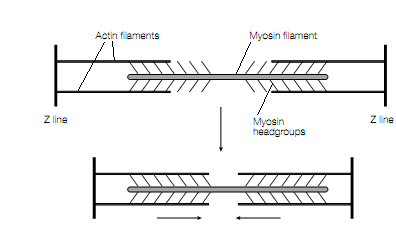
Schematic diagram indicating the interaction of the myosin thick filaments and the actin thin filaments during skeletal muscle contraction.