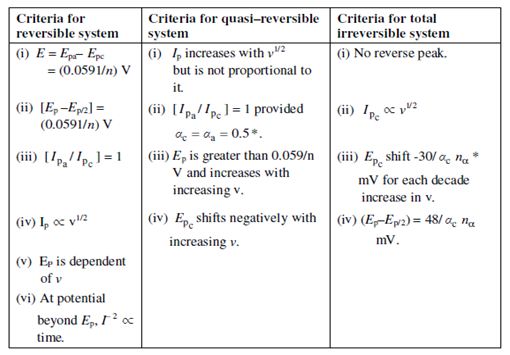
Diagnostic test to decide the reversibility of a redox reaction by cyclic voltammetry:
* A notations have their usual meaning as described in the text
αc and αa are transport numbers of cation and anion respectively
nα is the number of electrons transferred upto, and involved, the rate determining step
Probably the most marked feature of a cyclic voltammogram of a total irreversible system is the total absence of a reverse peak. Therefore, such a feature on its own does not necessarily imply an irreversible electron transfer procedures, but could be because of a fast subsequent chemical reaction. Therefore, other tests must therefore be made.
In some cases, the anodic current is low as compared to the cathodic current. This is because throughout most of the experiment there is a concentration difference which drives back the reduced species away from the electrode, most of the reduced species produced in forward reduction process, thus, diffuse into the bulk solution and cannot be re-oxidized on the time scale of a cyclic voltammetric experiment during reverse direction, i.e. anodic process. Hence, it gives reduced anodic peak current as compared to cathodic peak current.