Ohm's Law:
The interdependence among voltage, current, and resistance in dc circuits is termed as Ohm's law, named after the scientist who apparently first expressed it. Three formulas represent this law:
E = IR
I = E/R
R = E/I
You require only recall the first of these formulas to be able to derive the others. The easiest way to remember is to learn the abbreviations E for emf, I for current, and R for resistance; and remember that they emerge in alphabetical order with the equals sign after the E. Therefore E = IR. It is significant to remember that you should use units of volts, amperes, and ohms in order for the Ohm's law to work right. When you use volts, milliamperes (mA), and ohms or kilovolts (kV), microamperes (µA), and megohms (M?), you cannot expect to acquire the correct answers. When the initial quantities are given in units other than volts, amperes, and ohms, you must transform to these units and then compute. After that, you can convert the units back again to whatever you like. For illustration, when you get 13.5 million ohms as a computed resistance, you may prefer to say that it is 13.5 megohms. Though, in the computation, you must use the number 13.5 million (or 1.35 x 107) and stick to ohms for the units.
PROBLEM:
Assume that the dc generator as shown in figure below generates 10 V and that the potentiometer is set to a value of 10 ?. Determine the current?
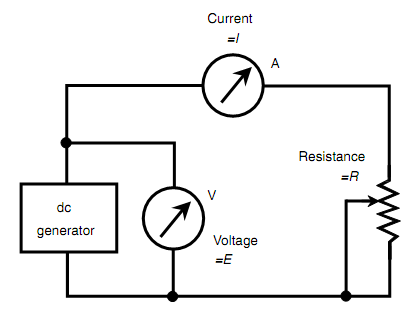
SOLUTION:
This is solved simply by using the formula I = E/R. Put the values of E and R; they are both 10, as the units are given in volts and ohms. Then
I =10/10 = 1.0 A.