Constructional Details of CMM
The construction of CMM might best be explained with the help of its two basic components:
(1) Probe and
(2) Mechanical structure.
Probe
The contact probe is a significant component of CMM. The probe is fastened to mechanical structure that permits movement of probe associated to the part. While contact has been made with part surface throughout measurement. The tip of the probe is built of ruby ball. Ruby is compose of Corundum (aluminum oxide). High hardness for wear resistance and low density for minimum inertia are the needed characteristics for the application of ruby in probe. Probe is of two kinds (1) single tip, and (2) multiple tips. Touch trigger probes are most broadly used probes. The probe actuates while the contact is made with part surface.
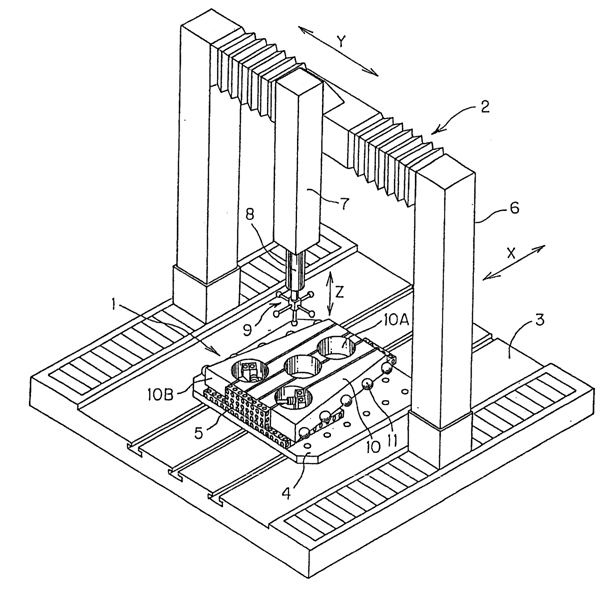
Figure: Coordinate Measuring Machine
The Several triggering mechanism, which are utilized commercially are discussed as follows.
1. The trigger is depend on the principle that, while the tip of the probe is deflected from neutral location then the highly sensitive electrical contact switch begin emitting signal.
2. The trigger actuates while there is an electrical contact among probe and metallic part surface.
3. The trigger uses a piezoelectric sensor that generates a signal based on tension or compression loading of the probe.
As contact presents between the probe and the surface of the object after that with the help of displacement transducer the coordinate location of the probe are accurately measured. Several displacement transducers such like optical scales, rotary encoding, and magnetic scales etc are utilized in CMM. Probe occupies its neutral position while it has been separate out from the contact surface.