Energy Conservation in Industries
Sporadic energy conservation efforts in the industrial sector have been taking place because of increasing awareness of the strong linkages among cost of production and energy usage. In the light of growing participation in the global economy, increased market pressure is largely responsible for motivating industries to find energy conservation measures for lowering their cost of production. Campaigns through the government and private institutions are also responsible for disseminating knowledge and promoting awareness of energy conservation measures.
Therefore, a precise national level picture on industrial efficiency is very hard to predict. One cannot ignore the large contribution of process efficiencies on the energy productivity indices that vary depending on the technology, sector, feed stocks age, management style and etc. There exists a crying require for in-depth research.
For example, a study was carried out to examine the potential for achieving energy efficiency through implementation of DSM options for HT consumers in Maharashtra. The options included energy efficient motors, variable speed drives, vapour absorption refrigeration systems (VARs), improved electric arc furnaces (EAFs), high efficiency fans and pumps, and industrial cogeneration (COGEN). The payback period for these options, according to the study, varied from 0.5 to 2.4 years along with an active DSM programme and among 0.6 to 4 years without a DSM programme. The study has developed a 5-year DSM plan with an estimated total cost of about $ 400 crores. The study reveals that the DSM plan would result in reductions of more than 9 million tonnes in CO2 emissions over the five-year period.
It goes without saying in which there is considerable room for improving the energy efficiency of our industries. Studies reveal which up to 75 percent of electricity use in industry is through motors and motor driven systems. Another 11% is by electrolysis, 9% through lighting and 3% through electric melting furnaces.
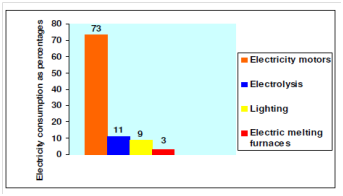
Figure: Electricity Consumption in Various Activities in Industries
In the recent years, some efforts have been made for the diffusion of energy efficient technologies in motor drives, energy efficient lighting systems and procedure changes. Some measures which are being taken and could be undertaken through the industries to curtail electricity consumption are:
1 Installation of variable frequency drive;
2 Installation of vapour absorption systems;
3 Upgrading co-generation facilities;
4 installations of auto/manual Star-Delta converters;
5 uses of high efficiency pumps and blowers;
6 lighting modifications;
7 replacing electrical heaters; and
8 installing capacitors.
Several industries (e.g., the steel industry) use large amounts of electricity to power several specialized processes at high temperatures. In several cases, such requirements exceed those of the buildings where the activities are housed and of the people inside them. Industries could resort to methods like 'cascading' of energy uses, where 'waste' heat from a high-temperature process is used to gives energy for lower temperature processes.
High-efficiency electric motors, pumps, fans and drive systems can be used along with accurate matching of motors to the tasks they are needed to perform, and accurate sizing of pipes and their associated pumps. This calls for energy use optimisation at all possible levels through choosing the best suited energy practices vetted through effective energy simulation models.