CNC Machines and Tool Handling Systems
Numerical Control (NC)
Numerical Control (NC) systems are hardware controls in which mostly functions are carried out by electronic hardware depend upon digital circuit technology. Numerical Control is a technique for controlling machine tools or processes by using coded command instructions. These coded command instructions are interpreted & converted by NC controller into two kinds of signals namely; motion control signals & miscellaneous control signals.
Motion control signals are a series of electric pulse trains that are utilized to control the positions and the speed of the machine table & spindle, while miscellaneous control signals are set of ON/OFF signals to execute the spindle rotation & direction, selection of cutting tools, control of coolant supply, automatic clamping & unclamping, etc. In motion control signals, every pulse activates a motion of one basic length-unit (BLU). Given figure represents a typical NC system.
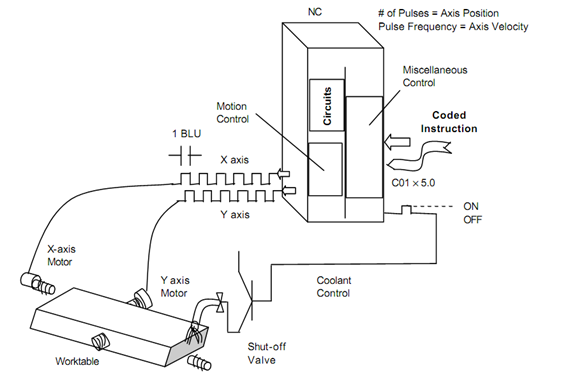
Numerical Control Systems
Computer Numerical Control (CNC)
CNC controls are soft-wired NC systems as control functions are controlled through software programs. On the other hand, Computer Numerical Control is the numerical control system in which dedicated, stored program microprocessors are made into the control to carry out basic and advanced NC functions. In CNC systems, Control signals are in the form of binary words, where every word contains fixed number of bits, 32 bits or 64 bits are commonly utilized, representing different axial positions.
For instance, BLU= 0.0001 inch. This represents motion up to 429 469 inch possible motions.
Objectives
After learning this unit, you must be able to
- Define various types of CNC operations,
- Understand the uses of CNC system elements,
- Classify the various types of CNC machines,
- Recognize the advantages and limitations of CNC machines, and
- Define tool handling systems and their uses in CNC machining operations.