Rotary Compressor:
Rotary compressors refer to positive displacement, direct-drive machines. There are basically two designs of this compressor:
(1) Rolling piston type
(2) Rotating vane type
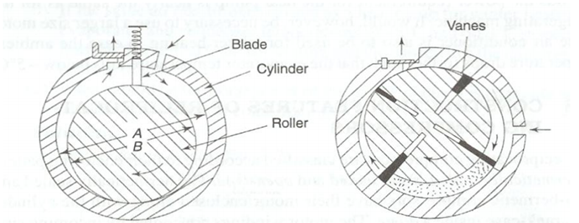
Rolling piston type Rotating vane type
Rotary Compressor
In the rolling piston type, as shown in fig the roller is mounted on an eccentric shaft having a single blade that is always in contact along the roller by means of a spring. The theoretical piston displacement is following
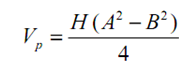
here A & B refers for respectively the diameters of the cylinder and rolling piston and H is for the length of the cylinder.
In the rotating vane type, shown in fig having four vanes, the rotor is concentric along the shaft. The vanes slide in the rotor but keep contact along the cylinder. The assembly of rotor & the vanes is off-centre w. r. t. the cylinder.
In both of the designs, the entire assembly is enclosed in a housing (not shown in the figures), filled up with oil & remaining is submerged in oil. An oil film forms the seal among the high-pressure & the low-pressure sides. While the compressor stops, this seal is lost & the pressure equalizes.
Rotary compressors contain high volumetric efficiencies because of negligible clearance. Normally they are used in a single stage up to a capacity of 5 TR having R-114. Large rotary compressors are utilized in low-temperature fields, such as in chemical & industrial processing, freezing and cold storages, as high displacement. low- stage or booster compressors at the temperature -900C to -l00°C evaporator temperature having R-12, R-22 & ammonia. They are available in 10 to 600 hp sizes along 2 to 120 cubic metres per minute displacement in one unit.