Euler's Theory:
One of the previous mathematical explanations of the phenomenon of buckling was given by Euler (1759) who proposed the following formula.
fE =PE/A = k(π2 EI/Al2) = k (π2 E/(1/r)2) =k π2 E/ λ 2
where fE = Euler's critical stress,
PE = Euler's critical load,
A = Area of cross section,
I = Moment of inertia of the section,
r =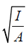 = Radius of gyration,
= Radius of gyration,
λ= le/ r = Slenderness ratio of the element, and
k = A coefficient which depends upon the end condition of the column.
Also various empirical formulae, example for Rankine's, Johnson's and Perry's are available for estimating the buckling load of columns.