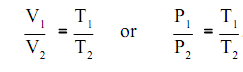Boyle's and Charles' Laws
The outcomes of certain experiments with gases at relatively low pressure lead Robert Boyle to formulate a familiar law. It defines that:
The pressure of a gas expanding at constant temperature differs inversely to the volume, or
(P1 )(V1 ) = (P2 )(V2 ) = (P3 )(V3 ) = constant.
The outcome of Charles's experimentation also concluded that:
The pressure of a gas differs directly with temperature whenever the volume is held constant, and the volume differs directly with temperature whenever the pressure is held constant, or