Feeders
Feeders route the power from the substation throughout the service area. They are classically either overhead distribution lines mounted on wooden poles, or underground buried or ducted cable sets. Feeders operate at the basically distribution voltage in primary distribution system and secondary distribution voltage within the secondary distribution system.
Definition of a feeder
Through definition, the feeder consists of all primary or secondary voltage level segments of distribution lines among two substations or among a substation and an open point (switch).
The most general primary distribution voltages in use are 11 kV, 22 kV and 33 kV. The major feeder that consists of three phases might branch into various main routes.
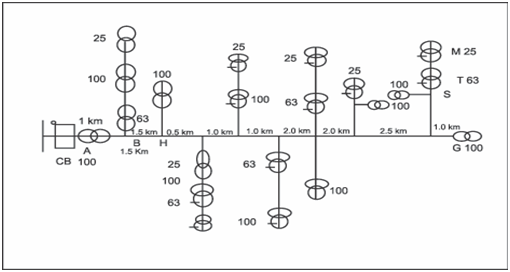
Figure: Typical layout of feeders in a primary distribution system (numbers indicate transformer capacities)
The major branches end at open points whereas the feeder meets the ends of other feeders - points at that a generally open switch serves as an emergency tie among two feeders.