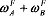Process of Reaching Equilibrium Through Trade:
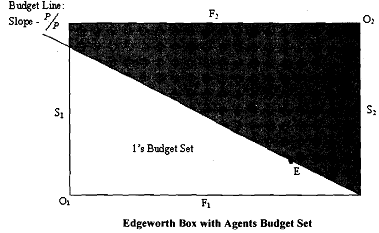
You have already seen the task assigned to an auctioneer for deciding the equilibrium prices. We apply the same logic to our example of food (F) and shelter (S) for reading the contract curve. See that in the position of initial endowment, all the goods are consumed. In this sense, the market clears.
However, such an allocation is not Pareto efficient. Therefore, the auctioneer announces some price after which both the parties trade. What they preferred at such prices might be Pareto efficient but not necessarily market clearing. So, there must be re-auction at new set of prices. To understand the price adjustment mechanism of the auctioneer, which ultimately produces an equilibrium, you may recall the option of charging the relative price. According to the position of excess demand, price, in our example PF/PS, will have to be varied. When the auctioneer get the price ratio correct, the market clears and there is no excess demand or supply for any good.
Example: (Due to Edgar Preugschat Lecture Notes)
We continue with an economy with 2 agents, 2 goods presented in the Edgeworth box. Present consumer i's problem as
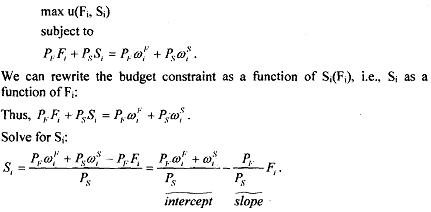
It will useful to recall the utility maximisation problem seen in case of individual consumer. It was seen that the slope of the budget line was determined by the negative of the price ratio. If you bring in the contrast now, the increment depends on both, the prices and the endowments of the goods. So, to tind the budget line, we need to find the endowment point in the two-,
goods diagram. Then, given the slope by the price ratio, draw the budget line through the endowment point.
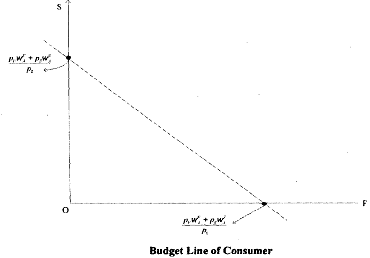
Note that you can consume your endowment independent price. So,
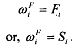
Now we bring together the budget line of two consumers in the Edgeworth box. In Figure 18.5 the two 2-goods diagrams are put-together. The size of the box is determined by the endowments.
The axes for F and S are of length equals to the sum of the endowments, i.e., the length of the F side is 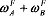 and the length of the s side is
and the length of the s side is