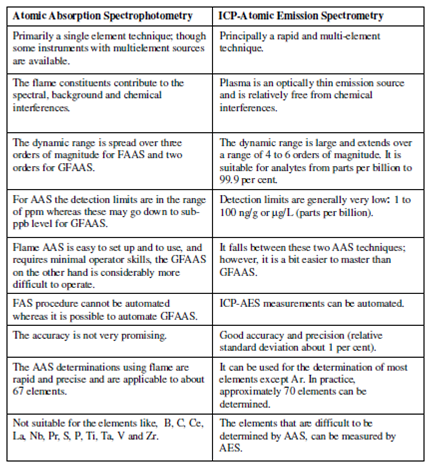
Different techniques as GFAAS:
More so at the operating high temperatures of ICP torch, even the most refractory elements are atomised along with high efficiency. As a output, detection limits for these refractory elements can be of the orders of magnitude lower with ICP than with FAAS methods. These may be at the 1-10 parts per billion levels. We can safely generalise the order of detection limits of different techniques as GFAAS (sub-ppb) > ICP-AES (1-10 ppb) > FAAS (sub-ppm).
In addition, the dynamic range of the various techniques is also important, as it directly affects the amount of dilution required in preparing solutions for analysis. If the dynamic linear range is quite wide, we might use fewer standards. The dynamic ranges of FAAS and GFAAS are of the order of only 102-103 only whereas the same for ICP- AES the dynamic range spreads upto 106. This makes it an appropriate technique which is capable of measuring from trace to percent levels. A comparative account of the characteristics of AAS and ICP-AES are briefly summarized in Table.
Table: A comparative account of the characteristics of AAS and ICP-AES