Transformation of a Colour Model:
The pixel value Vi (which is associated to the voltage of the deflection beam) is associated to the intensity level Ii by the following equation:
Vi= (Ic/C) 1/ γ
The values C & γ based on the display in use. If the raster display has no lookup table, Vi (e.g., 00010111 in an eight-plane display) is placed directly in the proper pixel. If there is a table, i is placed in the pixel and Vi is placed in entry i of the table. Use of the lookup table in this manner is called as gamma correction, after the exponent in Eq.
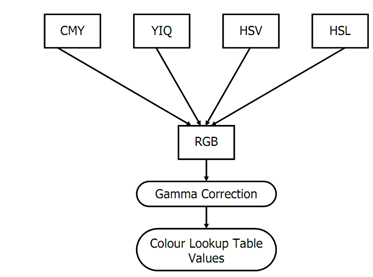
Figure: Transformation of a Colour Model to RGB
Chromatic colours generate more pleasing effects on the human vision system than achromatic colours. Though, they are more complex to study and generate. Colour is made by taking advantage of the fundamental trichromacy of the human eye. Three different coloured images are combined additively at photo-receptors in the eye to form a single perceived image whose colour is a combination of the three prime colours. Each of the three images is created by electron gun working on a colour phosphor. By using shadow-mask technology, this is possible to make the images intermingle on the screen, causing the colours to mix together because of spatial proximity. Well-saturated red, green, and blue colours are typically utilized to produce the wide range of desired colours.