Spring Subjected to Axial Load:
Let us consider a close coil helical spring subjected to axial load W.
Let R = Mean coil radius,
D = Mean coil diameter,
d = Wire diameter,
n = Number of coil,
l = Length of the wire,
α = Helix angle, and
Δ = Axial deflection.
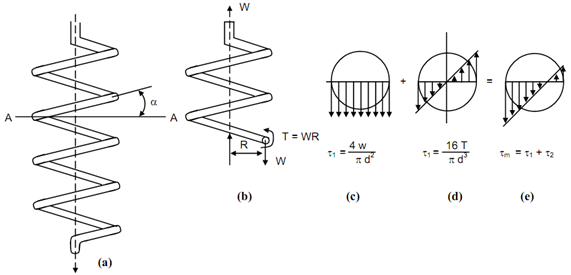
Figure: Close Coiled Helical Spring under Axial Load
Figure (a) illustrates a helical spring schematically. The force W acts along axis of the spring. Though in practice the axis may assume any position, for convenience this is regarded vertical AA represents a horizontal plane. α is the helix angle which is built by a coil with the horizontal plane. The angle is exaggerated in the given figure. It is in fact smaller. In practice, the close coiled helical carrying tensile load contains their coils touching each other. The compression springs can have some clearance among the coils.
Figure (b) shows the spring lower portion cut after second coil, therefore, the spring wire section, which is circular is exposed. In a close coiled spring a normal on the section shall be horizontal. It can be pointed out that if spring is open coiled then the section cut by a vertical plane shall not be a circle but a larger section. The Figure (c) is free body diagram on which an upward force W is axial & is balanced from a downward force W on the section in its plane and a moment T = W R working on the section around its axis.