Polyacrylamide gels (Bio-Gel):
Cross linked polyacrylamides form gels with water and are known as Bio-gels. They are mainly used for biochemical work. Unlike the Sephadex gels, these are fully synthetic and made by acrylamide, H2C = CH - CO - NH2. It is synthesized by copolymerizing acrylamide with the crosslinking agent N, N ′ -methylene-bis- acrylamide (H2C = CH - CO - NH - CH2 - NH - CO - CH = CH2). The concentration of the monomer can be varied to give different swelling characteristics and chromatographic characteristics. A partial structure of Bio-Gel is shown in Figure.
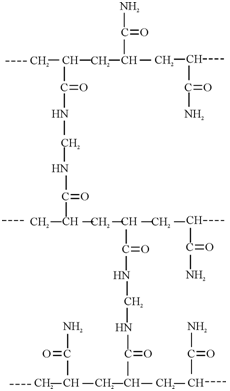
Figure: A schematic representation of partial structure of Bio-Gel
Bio-Gels are available from Bio-Rad Laboratories. They are produced by bead polymerization and are available as powder. They have a marked tendency to stick together and form lumps. Such as Sephadex, Bio Gel is xerogel.
While the dry powder is immersed in water, that swells to form the gel. Bio-Gel is quite inert and the weakest point for chemical reaction is the amide groups that are hydrolyzed at extremes of pH. At hydrolysis, the carboxyl groups created impart the ion exchange character.