Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS):
Within AFS, the gaseous atoms are excited to higher energy level through absorption of the electromagnetic radiation and the fluorescence emission from these excited atoms is measured. The major advantage of fluorescence detection compared to absorption measurements is the greater sensitivity achievable since the fluorescence signal has an extremely low background radiation. Here a schematic representation of the transitions related along with the phenomenon of atomic emission, atomic absorption, and atomic fluorescence emission is given in figure.
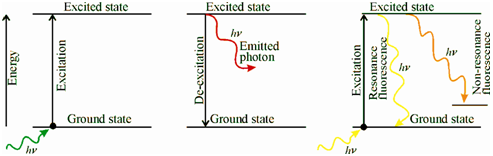
(a) (b) (c)
Figure: Schematic representation of the transitions in atomic (a) absorption, (b) emission and (c) fluorescence (resonance and nonresonance) emission
As we have a number of techniques of atomisation and three various ways viz., absorption, emission and fluorescence emission, of measuring the radiation analyte interaction, there are a number of various kinds of atomic spectroscopic methods. The category of atomic spectroscopic method is determined both through the method of atomisation as well as the nature of the interaction. For instance, an atomic spectroscopic method using electrothermal atomisation method and studying the fluorescence emission of radiation would be known as electrothermal atomic fluorescence spectroscopy.